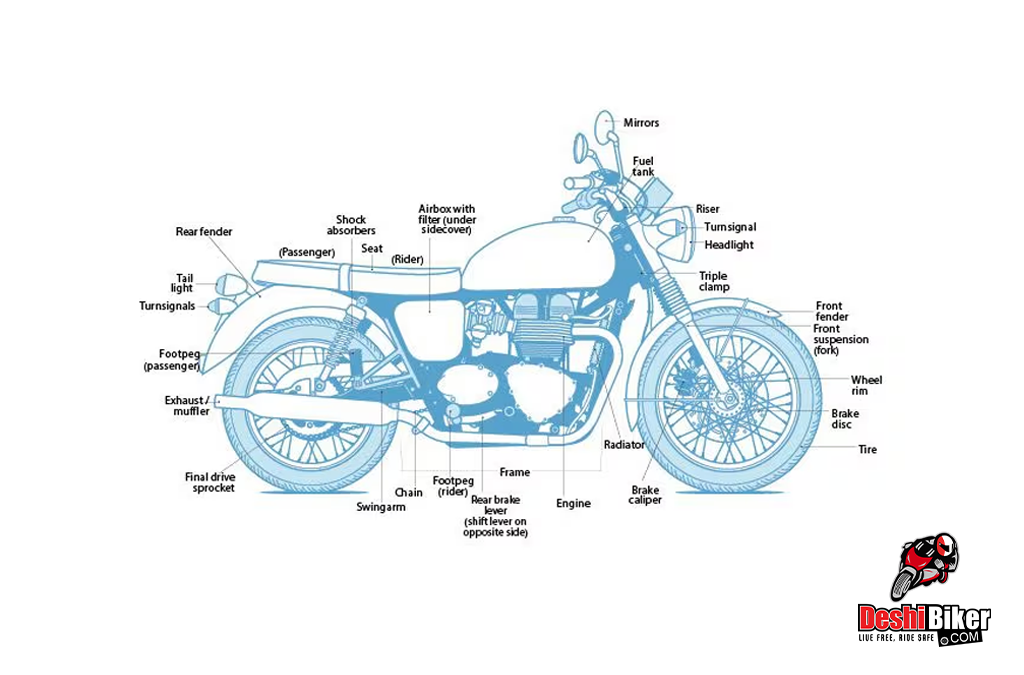
How many parts are in a motorcycle? A bike has many parts, to be precise, in double figures. What is the name of motorcycle parts? What are the major parts or components of a bike? Also, What is the most important part of a motorcycle? In this content, Deshi Biker will reveal the list of all the parts names of a motorcycle with their respective pictures or photos.
What are the Main Parts of a Bike?
There are some key parts that consist of different components or parts and are the major & mention-worthy parts. Those include:
| Name of Major Parts of a Bike | Purpose |
| Engine | It provides the power of the bike. They call it the heart of the bike. |
| Seat | It’s the place where the rider and the pillion sit. |
| Fuel Tank | The fuel is stored in this component. |
| Brakes | There are handbrakes and legbrakes. They help stop the bike or decrease the speed while required. |
| Headlights | During the dark condition, the rider needs to see clearly and the headlight offers him light. |
| Handlebars | Let the riders steer the motorcycle. That’s where the rider holds the bike while driving. |
| Suspension | Absorbs the bumps of the uneven conditions on the road. |
| Wheels | It helps move the bike smoothly and also offers stability. |
Motorcycle All Parts Name List
| Bike Parts Name | Type of Part |
| Engine | Engine and Power Component |
| Sprockets | Engine and Power Component |
| Oil Filter | Engine and Power Component |
| Muffler | Engine and Power Component |
| Oil Cooler | Engine and Power Component |
| Clutch | Control Component |
| Throttle | Control Component |
| Starter Paddle | Control Component |
| Brake Cable | Control Component |
| Handlebars | Control Component |
| Speedometer | Control Component |
| Front Brake | Control Component |
| Rear Brake | Control Component |
| Grips | Control Component |
| Gear Shift Lever | Control Component |
| Toolkit | Control Component |
| Brake Rod | Control Component |
| Battery | Electrical Part |
| Headlight | Electrical Part |
| Indicators / Turn Light | Electrical Part |
| Horn | Electrical Part |
| Ignition Switch | Electrical Part |
| Tail Light | Electrical Part |
| Starter Motor | Electrical Part |
| Spark Plugs | Electrical Part |
| Tachometer | Electrical Part |
| Stator | Electrical Part |
| Fuel Gauge | Electrical Part |
| Frame | Structural Component |
| Foot Pegs | Structural Component |
| Triple Tree | Structural Component |
| Kickstand | Structural Component |
| Safety Bar | Structural Component |
| Forks | Structural Component |
| Seat | Other Component |
| Fuel Cap | Other Component |
| Rim | Other Component |
| Tube | Other Component |
| Fuel Tank | Other Component |
| Key | Other Component |
| Front Fender | Other Component |
Motorcycle Parts Name List With Picture
Here is the short detail of each and every part or component found on a bike or motorcycle.
Clutch
Helps the rider to control the bike’s speed and also to change the gears. Associated with the engagement or disengagement of power to the wheels.
Throttle
This is the accelerator of the motorcycle. Its twisting movement determines the bike’s speed, and how fast the rider wanna go.
Handlebars
The riders hold onto it. It directs the movement of the bike, leftward, rightward, or straight.
Front Brake
This brake is for the front wheel. Generally controlled by the right hand of the biker. Helps to halt the bike, especially at higher velocity.
Rear Brake
The most vital braking part. It is used for the back or rear wheel of the bike. This brake based on applied pressure slows down the motorcycle or completely stops it.
Brake Cable
It connects the brake lever to the braking system. Thus it has great importance in stopping or slowing down the bike.
Speedometer
Locates at the dashboard. It shows the speed at which the bike is moving. Thus it is important as it lets the bikers keep the speed within the limit.
Gear Shift Lever
The rider uses this pedal to shift the gears which eventually lets control the speed as well as the torque.
Starter Paddle
With this component, the bikers manually start the bike. With a firm push or more precisely a kick at the right side, the bike starts. In the past, bikes used to be started with this but now with an automatic starting system bikers use it rarely.
Brake Rod
It’s a connecting rod. When you press the brake, actually this rod helps turn that into a braking mechanism. Thus it is an important component for helping to halt the motorcycle.
Grips
You see them at the end of both handlebars. Riders exactly hold onto those. Making sure a firm grip, guarantees safe handling and proper controlling.
Toolkit
The essential tools for repairing and maintaining the bike are contained in it. It’s like the first-aid box for the motorbike.
Engine
This component doesn’t need further detail to recognize. An engine is the most important component or part of the bike. It burns the fuel and generates the power and eventually lets the bike move forward.
Oil Cooler
It cools the engine to maintain the optimal temperature and avoid heating issues. For a smoother performance, it is of great importance.
Oil Filter
It cleans the engine oil keeping clean oil circulates and trapping the impurities.
Sprockets
These are the toothed wheels attached to the chain. Helps to transfer power from the engine to the back wheel alongside the wheel.
Muffler
It reduces the noise of the motorcycle. The exhaust gases from the engine generate bothering noises. Muffler decrease the level of those noises.
Frame
This is the major structural component of a motorcycle. Attaching & capturing all the parts of a motorbike together, it provides stability and also the shape of the body.
Safety Bar
It’s a protective feature. However, you’d see it in most of the modern bikes. Comes with a view to safeguarding both the rider. It also protects the bike when it accidentally falls.
Forks
Located at the front of the bike. It supports the front wheel. Also offers a smoother ride thanks to its shock-absorbing ability.
Triple Tree
Attaches the the handlebars and the forks with the bike’s frame. Responsible for playing a pivotal role in steering and maneuvering.
Kickstand
Lets the bike stay upright when the user parks it.
Foot Pegs
That’s where the rider’s feet are rested. Very much needed for a relaxing journey and also useful for better controlling indeed.
Battery
This is the source of the energy of the bike. It powers all the electrical components of the bike including light, horn, indicators, etc. It also helps you have an automated start with a switch even without a kick-start.
Headlight
Located right at the very front. It shows the rider the light during darkness. It’s a must for the nighttime or foggy rides.
Indicators or Turn Signals
Stays in a pair on both the front and rear sides. It gives the other users of the road the signal, exactly which side the bike will be heading. Indicates the turn or lane changing direction.
Horn
It is a sound alert system. With a press, it creates a sound that notifies other users of the road about the vehicle’s existence.
Tail Light
Located at the very rear end. It reveals the bike’s presence especially in the night or foggy condition when visibility is less than normal.
Fuel Gauge
Shows how much fuel is there in the tank. Hence notifies you when you need to refill your tank. Without this component, the user would never know when they are required to take fuel unless the bike has completely stopped midway.
Spark Plugs
This little component ignites the fuel. It enables the engine to run and with a faulty plug, the bike won’t start smoothly.
Tachometer
Reveals the rotation speed of the engine’s crankshaft. Thus it indicates you and helps you to maintain an optimal engine speed.
Ignition Switch
It actually starts or stops the engine of the motorcycle. It’s where you insert the key.
Stator
Produces the power for the battery and is helpful to keep the electrical elements of the biker functional.
Starter Motor
You can activate it by pressing the start button of the motorcycle. It jumpstarts the engine.
Rim
The bike’s wheel’s outer circular edge. Holds the tire securely in its absolute position. Offers stability and proper alignment.
Tube
It’s present in the inside part of the tire. This is filled with air. Required for the bike’s stability and it helps maintain proper air pressure.
Seat
It’s where the rider sits. The pillion also sits in this cushioned area.
Key
With its insertion inside the ignition switch, the bike gets its life. You can’t start the bike legally without the key.
Fuel Tank
This is the storehouse of the fuel of the bike. Based on the bike type, users store petrol, diesel, or octane there.
Fuel Cap
This is the lid of the fuel tank and keeps the fuel safely inside the tank. The user removes it temporarily while refueling and then places it right in its position.